Dolphins are among the most intelligent and agile marine mammals on Earth. What makes them such extraordinary survivors is their suite of evolutionary traits known as dolphin adaptations. These adaptations allow them to thrive in various aquatic environments—from the open ocean to freshwater rivers. In this article, we’ll explore key dolphin adaptations for survival, including structural, behavioral, and physical changes across different species such as the bottlenose dolphin, spinner dolphin, pink dolphin, and the elusive Amazon river dolphin.
Table of Contents
What Are Dolphin Adaptations?
Dolphin adaptations are specialized characteristics that evolved over millions of years to help dolphins live, hunt, communicate, and avoid predators in aquatic habitats. These adaptations are typically categorized into:
- Structural adaptations (body form and physical traits)
- Behavioral adaptations (actions and social behavior)
- Physiological adaptations (internal functions and biological processes)
These combined features give dolphins an edge in the marine ecosystem.
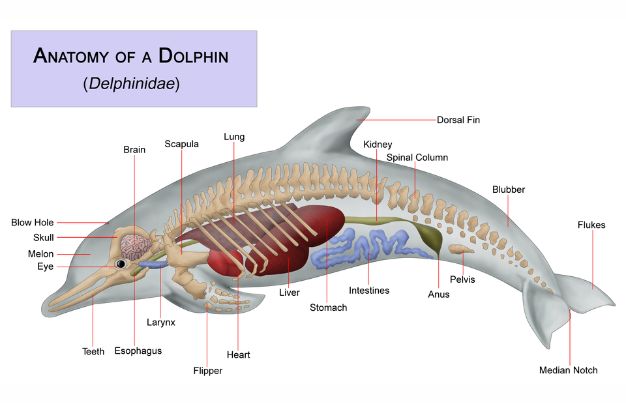
Structural Dolphin Adaptations That Help Them Survive
Structural adaptations in dolphins are essential for life in water. Here are a few crucial ones:
Streamlined Body Shape
Dolphins have a hydrodynamic body that minimizes water resistance, allowing swift and smooth movement through the water.
Dorsal Fin and Flippers
The dorsal fin stabilizes the dolphin while swimming, and the pectoral flippers help with steering. The tail fluke powers their propulsion.
Blowhole for Breathing
Instead of a nose, dolphins breathe through a blowhole located on top of their head—an excellent adaptation for quick surfacing.
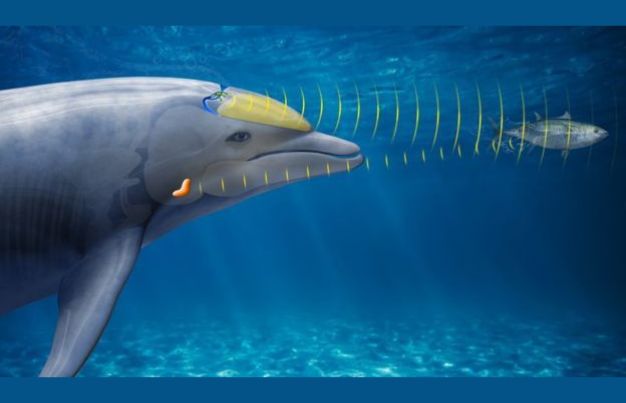
Echolocation Ability
Dolphins emit sound waves and listen for their echoes to navigate, hunt, and communicate. This is especially useful in murky waters.
Behavioral Dolphin Adaptations: Social Brilliance in the Sea
Dolphins are highly social creatures. Their behavioral adaptations are rooted in complex social structures and learned communication.
Pod Living
Most dolphins live in groups called pods. This behavior enhances protection, social bonding, and cooperative hunting.
Communication Skills
Using a combination of clicks, whistles, and body language, dolphins communicate effectively. Each dolphin even has a signature whistle, like a name.
Play and Learning
Play is common in dolphin pods and serves as a method of learning survival skills, including coordination and teamwork.
5 Key Dolphin Adaptations for Survival
Understanding how dolphins survive in the wild involves examining their top adaptations:
1. Echolocation for Navigation
Especially critical for dolphins in muddy rivers or nighttime hunting.
2. Blubber for Insulation
A thick layer of fat keeps them warm in cold waters.
3. High Intelligence
Problem-solving abilities and emotional intelligence aid survival.
4. Speed and Agility
Some species, like the spinner dolphin, can leap and spin to escape predators.
5. Breathing Control
Dolphins consciously control their breath, preventing drowning during deep dives.

Bottlenose Dolphin Adaptations: The Generalists of the Ocean
The bottlenose dolphin is perhaps the most studied species. Its adaptations include:
- A robust body suited for coastal and open-sea life.
- Broad dietary preferences, enabling them to eat fish, squid, and crustaceans.
- Use of tools, such as sea sponges to protect their snouts while foraging.
Their adaptability has made them the dominant dolphin species worldwide.
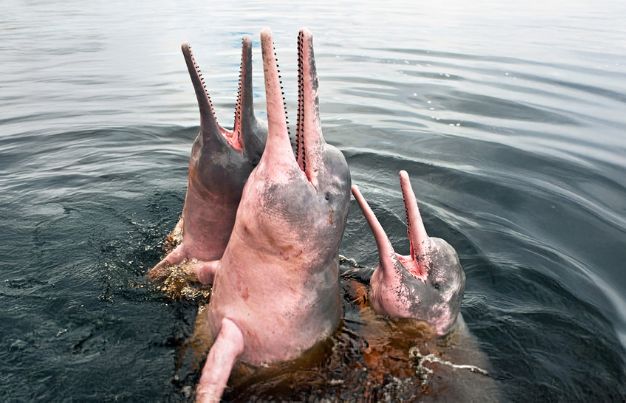
Amazon River Dolphin Adaptation: Masters of Freshwater
Also known as the pink river dolphin, this unique species exhibits special adaptations:
Flexible Neck
Unlike oceanic dolphins, the Amazon dolphin’s neck vertebrae are unfused, allowing it to move its head side-to-side to navigate narrow waterways.
Reduced Dorsal Fin
A smaller dorsal fin prevents it from getting entangled in submerged vegetation.
Rosy Pigmentation
Thought to be a result of capillary density and scar tissue, their pink color offers camouflage in the sediment-filled rivers.

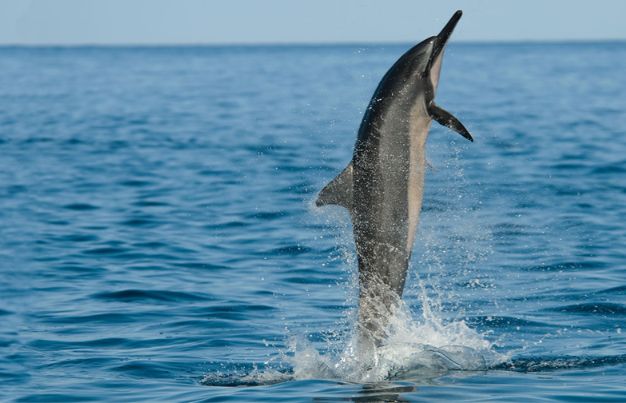
Spinner Dolphin Adaptation: Acrobatics with a Purpose
The spinner dolphin is famous for its mid-air spins. But why do they spin?
- To dislodge parasites
- As a form of communication
- Possibly for courtship displays
Their lightweight frame and strong tail muscles make these spins possible—an excellent example of behavioral and physical adaptation.
Dolphin Adaptations for Kids: A Simple Overview
For educational purposes, here’s a simplified version of dolphin adaptations for kids:
- Blowhole: Helps them breathe
- Flippers and flukes: Help them swim
- Echolocation: Like a built-in GPS
- Pods: Like dolphin families
- Blubber: Keeps them warm
These traits are great for school projects or early biology lessons.
Pink Dolphin Adaptation: Not Just a Pretty Color
The pink dolphin, a type of Amazon river dolphin, shows extreme adaptations for its unique environment:
- Enhanced echolocation for murky water
- Sharp, interlocking teeth for catching slippery fish
- High maneuverability to avoid obstacles in rivers
This makes them one of the most fascinating examples of species-specific dolphin adaptations.
Conclusion: Why Dolphin Adaptations Matter
Dolphins are evolutionary marvels. Each species, from the agile spinner dolphin to the mysterious Amazon river dolphin, showcases a unique blend of dolphin adaptations that allow it to survive and thrive. Whether it’s their communication skills, structural design, or pink coloration, every trait has a purpose in their environment.
Understanding dolphin adaptations not only enriches our knowledge of marine biology but also inspires conservation efforts for these intelligent beings who share our planet.
FAQs About Dolphin
1. What are the adaptations of a dolphin?
Dolphin adaptations include echolocation, streamlined bodies, blubber insulation, strong social behavior, and the ability to live in salt and freshwater environments.
2. What are the structural adaptations of a dolphin?
These include a streamlined body, dorsal fin for stability, flippers for steering, blowhole for breathing, and a powerful fluke for propulsion.
3. What are 3 adaptations of a dolphin?
Three main adaptations are echolocation, blubber for warmth, and social living in pods for cooperative defense and hunting.
4. What are the behavioral adaptations of a dolphin?
Behavioral adaptations include cooperative hunting, pod communication using whistles, playful behavior, and tool usage in foraging.
5. What are physical adaptations of a dolphin?
Physical adaptations involve internal and external structures like blubber, muscular tails, sharp teeth (in some species), and sonar navigation systems.









